Were you aware that mining one bitcoin can actually take years? That’s correct! The process of mining a single bitcoin using just one ASIC miner can be quite time-consuming due to the fierce competition and the high level of computational power involved.
So, how long does it actually take to mine one bitcoin? Let’s dive deeper into the factors that impact mining time and explore the fascinating world of bitcoin mining.
Key Takeaways:
- The time to mine one bitcoin can vary significantly based on several factors.
- The hashing power of the mining hardware, network hash rate, and mining difficulty all influence the mining time.
- Mining a full bitcoin on your own can be extremely challenging and time-consuming.
- Bitcoin mining is a process that involves solving cryptographic puzzles and producing blocks.
- Mining hardware and hash rate are crucial determinants of mining time and success.
Factors Affecting Bitcoin Mining Time
The time it takes to mine one bitcoin is influenced by several factors. These factors include the mining operation’s hash rate, the total network hash rate, and the Bitcoin mining difficulty.
The mining operation’s hash rate represents the computing power dedicated to mining. A higher hash rate allows for faster mining of bitcoins. The mining operation’s share of the network’s total computing power also plays a role in mining speed. The greater the mining operation’s share, the faster it can mine bitcoins.
Additionally, the Bitcoin mining difficulty and network hash rate impact the time it takes to mine one bitcoin. Bitcoin mining difficulty is adjusted approximately every two weeks to maintain an average block confirmation time of ten minutes. When the network hash rate increases, the mining difficulty adjusts, making it harder to mine bitcoins individually.
Factors Affecting Bitcoin Mining Time
| Factors | Impact on Mining Time |
|---|---|
| Mining Operation’s Hash Rate | A higher hash rate allows for faster mining. |
| Network Hash Rate | Higher network hash rate increases mining difficulty. |
| Bitcoin Mining Difficulty | Difficulty adjusts based on network hash rate to maintain a ten-minute block confirmation time. |
The Process of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is a fascinating process that secures the Bitcoin network and provides miners with newly minted bitcoins as a reward. Let’s dive into the details of how bitcoin is mined and the overall bitcoin mining process.
First and foremost, bitcoin is mined by solving cryptographic puzzles and adding verified transactions to the blockchain. The blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records all bitcoin transactions and ensures their immutability. Miners play a crucial role in validating and adding these transactions to the blockchain.
Miners use powerful computer systems, often specialized hardware called ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), to compete in solving complex mathematical puzzles. These puzzles require significant computational power and energy consumption. The miners compete with each other to be the first to find a solution and confirm a block of transactions.
Once a miner successfully solves a puzzle, they broadcast the solution to the network. Other nodes in the network verify the solution, ensuring its correctness. After verification, the block is added to the blockchain, making the transactions within the block official and immutable.
As a reward for their efforts, the miner who successfully mines a block receives a reward in the form of newly minted bitcoins. This block reward serves as an incentive for miners to continue dedicating their computing power to secure the network.
“Bitcoin mining: A complex process that involves solving cryptographic puzzles, validating transactions, and adding them to the blockchain.”
The bitcoin mining process is random, meaning that each attempt to solve a puzzle is independent of previous attempts. The probability of successfully mining a block is determined by the miner’s computational power and the overall network’s computing power.
In addition to the block reward, miners also earn transaction fees. When users initiate bitcoin transactions, they can attach fees as an incentive for miners to prioritize their transactions. Miners select transactions with higher transaction fees to include in the blocks they mine, maximizing their potential earnings.
Summary
In summary, bitcoin mining is the process of solving cryptographic puzzles and adding verified transactions to the blockchain. Miners use specialized hardware to compete in solving these puzzles and are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees. The mining process is independent for each block and requires substantial computational power. Without miners, the Bitcoin network would not function securely and efficiently.
Now that we understand the process of bitcoin mining, let’s explore the impact of mining hardware and hash rates in the next section.
Mining Hardware and Hash Rate
The success and efficiency of Bitcoin mining depend heavily on the mining hardware and its hash rate. Utilizing specialized hardware known as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), miners can maximize their mining capabilities. These ASICs are purpose-built for efficiently mining Bitcoins, providing a significant advantage over general-purpose hardware.
The hash rate plays a crucial role in determining the mining time for one Bitcoin. The hash rate refers to the speed at which a mining machine can solve the complex cryptographic puzzles required for mining. A higher hash rate translates to a higher computational capacity, increasing the chances of successfully mining at least one Bitcoin.
Investing in high-performance mining hardware with a substantial hash rate can significantly impact mining efficiency and profitability. Miners with advanced ASICs can process more calculations in a given timeframe, allowing them to mine more Bitcoins compared to those with lower hash rates.
Miners constantly seek hardware upgrades and optimizations to stay competitive in the mining ecosystem. The ever-evolving nature of Bitcoin mining necessitates staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in mining hardware technology to ensure optimal performance.
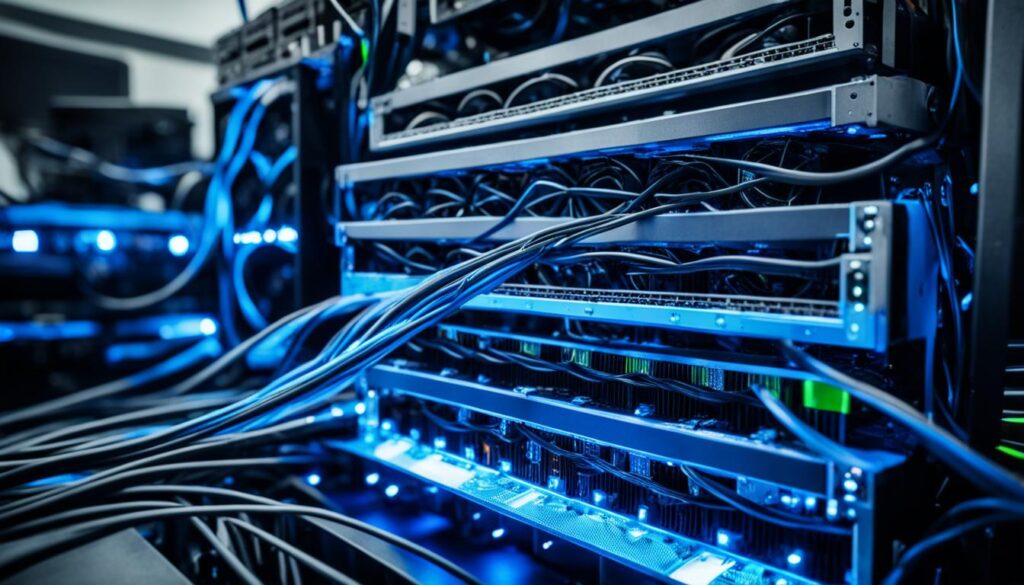

Comparison of Mining Hardware and Hash Rates
| Brand and Model | Hash Rate (GigaHashes per second) |
|---|---|
| Antminer S19 Pro | 110 |
| Bitmain Antminer S9 | 14 |
| MicroBT Whatsminer M30S | 86 |
| Ebang Ebit E12+ | 50 |
The table above showcases a comparison of popular mining hardware models and their corresponding hash rates. It is essential to consider the hash rate when selecting a mining hardware model, as it directly impacts mining efficiency and the potential to mine one Bitcoin within a reasonable timeframe.
Investing in high-performance mining hardware with a substantial hash rate is a strategic move for miners aiming to maximize their return on investment. By equipping themselves with powerful ASICs, miners can increase their chances of success and enhance their overall mining experience.
Bitcoin Mining Difficulty
Bitcoin mining difficulty plays a crucial role in the process of mining bitcoins. As the overall hash power of the network increases, the difficulty level adjusts to maintain a consistent average block confirmation time. This difficulty adjustment mechanism ensures that a new block is created approximately every ten minutes.
By factoring in the total hash power of the network, Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment algorithm regulates the level of mining difficulty. As more miners join the network and contribute their computing power, the individual share of each miner decreases. Consequently, mining bitcoins individually becomes harder due to the increased competition.
Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism is designed to prevent block confirmation time from being accelerated despite the increase in network hash power. This ensures a fair and consistent mining process for all participants.
How Does Difficulty Adjustment Work?
Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment algorithm recalculates the mining difficulty every 2016 blocks, or roughly every two weeks. The adjustment is based on the total hash power of the network during that period. If the network hash power increases significantly, the difficulty will adjust upwards to make mining more challenging.
The difficulty adjustment mechanism operates through a mathematical formula that compares the timestamp of the previous 2016th block with the current block’s timestamp. If the time taken to mine the previous 2016 blocks is shorter than two weeks, the difficulty increases. Conversely, if the time is longer than two weeks, the difficulty decreases to make mining easier.
This dynamic difficulty adjustment mechanism ensures that the time it takes to mine each block remains relatively consistent over time, regardless of changes in the network hash power.
Impact on Individual Miners
Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism has implications for individual miners. As the mining difficulty increases and individual mining shares decrease, it becomes more challenging to mine bitcoins independently. Mining pools, where miners combine their computing power, have become popular as they offer a better chance of mining bitcoins efficiently.
However, even with the difficulty adjustment mechanism, it is important to note that mining bitcoins is still a competitive process. Miners need to consider various factors, such as the efficiency of their mining hardware and electricity costs, to ensure profitability in the ever-evolving landscape of Bitcoin mining.
Ultimately, Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism is a fundamental aspect of the network’s design, providing stability and fairness to the mining process while adapting to changes in network hash power.

| Year | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 16,776,791,174,048 |
| 2021 | 25,046,217,920,000 |
| 2022 | 31,619,051,240,319 |
Impact of Bitcoin Price on Mining
When it comes to bitcoin mining, the price of bitcoin plays a pivotal role in determining the mining profitability. Miners need to cover their costs, which are often denominated in fiat currencies, and this is heavily influenced by the price of bitcoin. Let’s take a closer look at how the price of bitcoin impacts the mining landscape.
1. Mining Profitability:
The profitability of mining is directly tied to the price of bitcoin. When the price drops, mining can become unprofitable for many miners. Bitcoin price impact on mining is significant, as it affects the revenue generated from mining operations.
2. Hash Rate and Mining Difficulty:
As the price of bitcoin drops, many miners may find it unprofitable to continue mining. This leads to a decrease in the overall hash rate of the network and, subsequently, a decrease in mining difficulty. Conversely, when the price of bitcoin rises, more miners join the network to capitalize on the higher profitability. This increase in miners results in higher competition and increased mining difficulty.
“The price of bitcoin has a direct impact on the number of miners in the network. When prices are low, it becomes economically unfeasible for miners to continue their operations.”
3. Revenue Generation:
Miners generate revenue through two primary channels: block rewards and transaction fees. The block reward is a set amount of newly minted bitcoins that miners receive for successfully mining a new block. Bitcoin price impact on mining can affect the value of these block rewards. Additionally, miners earn transaction fees for processing transactions within the blocks they mine. The higher the price of bitcoin, the higher the value of these transaction fees, resulting in increased revenue for miners.
As we can see, the price of bitcoin has a direct impact on the profitability of mining operations. When the price falls, it can make mining unprofitable, leading to a decrease in mining activity. Conversely, when the price rises, more miners enter the network, resulting in increased competition and mining difficulty. Miners must carefully monitor the price of bitcoin to ensure their operations remain profitable.
Conclusion
In summary, the time it takes to mine one bitcoin can vary extensively depending on various factors. These factors include the mining hardware used, the hash rate of the mining operation, the network’s overall hash rate, the mining difficulty, and the price of bitcoin. Due to the high competition and the need for specialized equipment, it is challenging for individual miners to mine one bitcoin on their own.
However, miners can increase their chances by joining mining pools, where they combine their computing power to mine bitcoins collectively. Mining pools offer a better opportunity to earn rewards and cover the high costs associated with mining. Additionally, Bitcoin mining generates revenue through both block rewards, which are newly minted bitcoins, and transaction fees paid by users.
It’s important to understand that the profitability of bitcoin mining is closely tied to the price of bitcoin. When the price drops, it can become unprofitable for miners, leading to a reduction in hash rate and mining difficulty. Conversely, when the price rises, more miners join the network, increasing competition and mining difficulty. This dynamic relationship plays a crucial role in the overall mining ecosystem.
In conclusion, Bitcoin mining involves complex processes and requires careful consideration of various factors. Understanding the time it takes to mine one bitcoin and the key factors that impact mining efficiency is essential for miners and enthusiasts navigating this space.










