Did you know that only 55% of Americans have access to a workplace retirement plan?
With the decline of traditional pension plans and uncertainty surrounding Social Security, it’s essential to explore different IRA investment types for retirement planning. These investment options provide tax advantages and the opportunity to grow your savings over time.
Key Takeaways:
- Traditional IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions and tax-deferred earnings until retirement.
- Roth IRAs provide tax-free withdrawals in retirement but require after-tax contributions.
- SEP IRAs are ideal for self-employed individuals and small business owners.
- Self-directed IRAs allow for investing in a wide range of assets beyond traditional stocks and bonds.
- Individual 401(k)s offer higher contribution limits for self-employed individuals and business owners.
Understanding Traditional IRAs
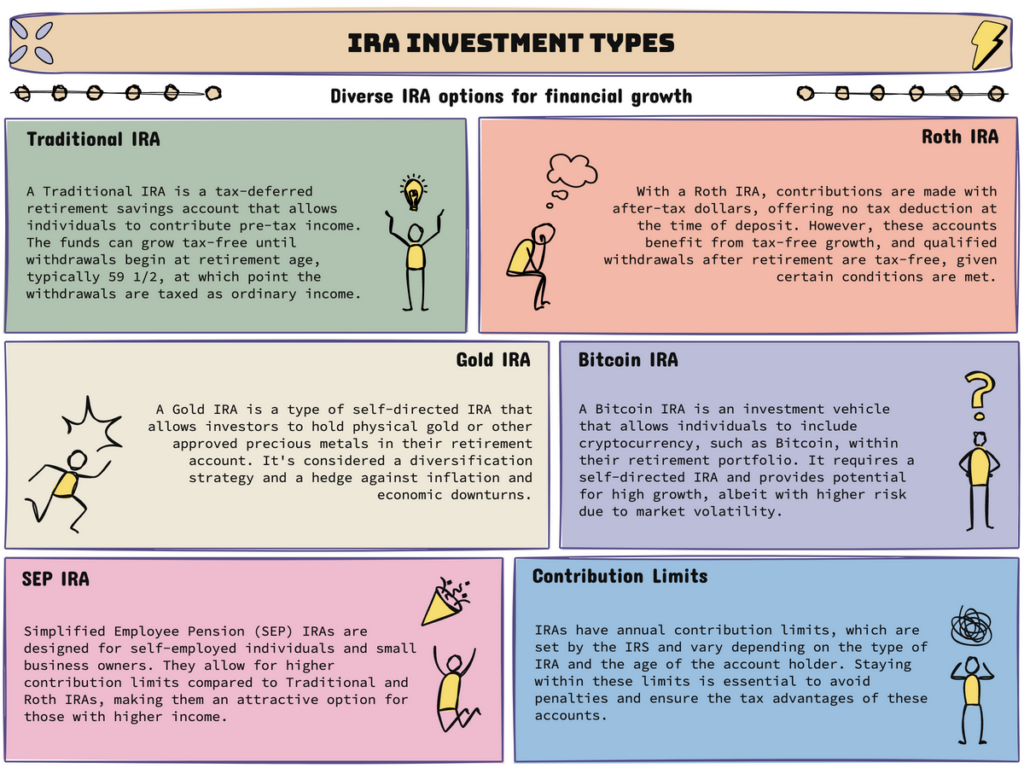
Traditional IRAs are among the most common retirement accounts available. They provide individuals with a tax-advantaged way to save for retirement. With a traditional IRA, individuals can set up an account at a financial institution and contribute money to be invested in their future.
One of the main benefits of a traditional IRA is the potential for tax deductions. Contributions to a traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, meaning they can lower an individual’s taxable income for the year. This can lead to potential tax savings, especially for those in higher tax brackets.
Another advantage of a traditional IRA is the tax-deferred growth of earnings. Any interest, dividends, or capital gains earned within the account are not subject to taxes until withdrawals are made in retirement. This allows the investments in the IRA to grow and compound over time without the drag of annual taxes.
It’s important to note that contributions to a traditional IRA are subject to annual limits set by the IRS. For the tax year 2021, the contribution limit for individuals under 50 is $6,000. Those aged 50 and older can make additional “catch-up” contributions of up to $1,000, bringing their total contribution limit to $7,000.
Contributions to a traditional IRA can be made up until the individual’s tax filing deadline, usually April 15th of the following year. However, it’s generally recommended to make contributions by the end of the calendar year to maximize the potential for tax deductions.
Tax-Deductible Contributions
Contributions made to a traditional IRA can be tax-deductible, allowing individuals to lower their taxable income. The ability to deduct contributions depends on several factors, including income level, marital status, and access to an employer-sponsored retirement plan.
Tax-Deferred Growth
Earnings within a traditional IRA grow tax-deferred, meaning they are not subject to annual taxes. This allows the investments in the account to compound over time, potentially resulting in significant growth of the retirement savings.
| Year | Contribution Limit | Catch-Up Contributions (Age 50+) |
| 2021 | $6,000 | $1,000 |
| 2020 | $6,000 | $1,000 |
| 2019 | $6,000 | $1,000 |

Understanding the contribution limits of a traditional IRA is important for individuals planning their retirement savings strategy. By staying within these limits, individuals can take full advantage of the tax benefits and maximize their retirement nest egg.
Overall, traditional IRAs provide a valuable retirement savings tool, offering tax advantages and the potential for long-term growth. By contributing to a traditional IRA and taking advantage of tax deductions, individuals can take important steps towards building a secure and comfortable retirement.
Exploring Roth IRAs
When planning for retirement, it’s crucial to explore the various IRA investment options available. One popular choice is the Roth IRA. Unlike traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs offer unique tax advantages that can significantly benefit your retirement savings.
Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax money, meaning you’ve already paid taxes on the funds you contribute. However, the major advantage comes during retirement when qualified withdrawals from your Roth IRA are tax-free. This tax-free status makes Roth IRAs an excellent option for individuals looking to maximize their retirement savings while minimizing future tax liabilities.
Similar to traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs have an annual contribution limit set by the IRS. For 2021, the contribution limit is $6,000 for individuals under the age of 50, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 available for those aged 50 and older. By taking advantage of these contribution limits, you can steadily build your tax-free retirement nest egg.
A Roth IRA can be a valuable tool for individuals who anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement or those who want to diversify their retirement savings with tax-free withdrawals. It offers flexibility and peace of mind, knowing that your hard-earned savings can grow and be withdrawn tax-free when you need it most.”Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax money, but qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
The Benefits of a Roth IRA
There are several advantages to consider when exploring Roth IRAs:
- Tax-Free Withdrawals: Qualified withdrawals from a Roth IRA in retirement are entirely tax-free, providing increased financial flexibility.
- Tax Diversification: By combining both Roth and traditional IRAs, you can create a tax-diversified retirement portfolio, allowing for strategic tax planning.
- No Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Unlike traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs do not require you to take mandatory withdrawals during your lifetime, giving you more control over your retirement savings.
It’s important to note that Roth IRAs have specific eligibility requirements based on income. For individuals with a higher income, there may be limitations or restrictions on contributing to a Roth IRA. Consulting with a financial advisor can help clarify these eligibility requirements and assist you in making informed decisions.

Considering SEP IRAs
SEP IRAs, a type of retirement savings accounts, are a popular retirement savings option for self-employed individuals and small business owners. With the ability to contribute a percentage of income, SEP IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions that can help individuals maximize their retirement savings.
Unlike traditional and Roth IRAs, SEP IRAs have higher contribution limits, making them an attractive choice for self-employed individuals with fluctuating income. The contribution limit for SEP IRAs is determined by the IRS and can vary from year to year. It’s important to stay updated on the current contribution limit to make the most of this retirement savings opportunity.
One of the key advantages of SEP IRAs is the flexibility they offer. Contributions to a SEP IRA can be made on behalf of both the business owner and eligible employees. This makes SEP IRAs not only a valuable tool for self-employed individuals but also a way for small business owners to provide retirement benefits to their employees.
It’s worth noting that SEP IRAs are subject to certain rules and regulations. For example, contributions must be made by the due date of the employer’s tax return, including extensions. Additionally, employees who meet specific eligibility requirements must receive contributions proportional to their compensation.

In conclusion, SEP IRAs offer self-employed individuals and small business owners a tax-efficient retirement savings option. With higher contribution limits and the ability to provide retirement benefits to eligible employees, SEP IRAs can play a crucial role in building a secure financial future.
| Advantages of SEP IRAs | Considerations for SEP IRAs |
Tax-deductible contributionsHigher contribution limitsFlexibility to contribute on behalf of employeesPotential for significant retirement savings | Compliance with IRS regulationsEmployee eligibility requirementsContributions must be made by tax return due dateProportional contributions for eligible employees |
Exploring Self-Directed IRAs
Self-directed IRAs offer a unique opportunity for individuals to take control of their retirement investments and explore a diverse range of investment options beyond traditional stocks and bonds. With a self-directed IRA, you have the flexibility to invest in real estate, private equity, and even cryptocurrencies, opening up a world of possibilities for growing your retirement savings.
One of the advantages of a self-directed IRA is the ability to invest in real estate. Whether you’re looking to purchase rental properties, invest in a commercial building, or even own a vacation home, a self-directed IRA allows you to use your retirement funds to make these investments. By investing in real estate through your IRA, you can potentially benefit from rental income, property appreciation, and tax advantages.
With a self-directed IRA, investors have the freedom to diversify their retirement portfolio beyond traditional investments. Real estate has long been considered a stable and profitable investment, and leveraging it through a self-directed IRA can provide significant financial benefits.
In addition to real estate, a self-directed IRA also allows you to explore investment options such as private equity. This can involve investing in private companies, startups, or even venture capital funds. By diversifying your portfolio with these alternative investment options, you can potentially access higher returns and take advantage of unique opportunities. However, it’s important to note that these investments may carry a higher level of risk and should be thoroughly researched before committing your retirement funds.
Another intriguing investment option available through a self-directed IRA is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. As the popularity of digital currencies continues to grow, many investors are looking to include cryptocurrencies in their retirement portfolio. Investing in cryptocurrencies through a self-directed IRA allows you to capitalize on the potential for growth and diversify your investments, all within a tax-advantaged retirement account.
It’s important to remember that while self-directed IRAs offer greater control and investment flexibility, they also come with certain responsibilities and risks. You must ensure compliance with IRS regulations and conduct thorough due diligence on any investment opportunity to protect your retirement savings.
By exploring self-directed IRAs, investors can unlock unique investment opportunities and take a proactive approach to growing their retirement savings. Whether it’s real estate, private equity, or cryptocurrencies, a self-directed IRA provides the freedom to pursue alternative investments and potentially achieve greater financial success in retirement.

Benefits of Self-Directed IRAs:
- Flexibility to invest in real estate, private equity, and cryptocurrencies
- Potential for rental income, property appreciation, and tax advantages with real estate investments
- Diversification of your retirement portfolio with alternative investment options
- Potential for higher returns and unique investment opportunities
- Control and autonomy in managing your retirement investments
Understanding Individual 401(k)s
Individual 401(k)s, also known as solo 401(k)s, are retirement plans designed specifically for self-employed individuals or business owners with no employees other than a spouse. These plans offer unique advantages and higher contribution limits compared to traditional and Roth IRAs, making them a popular choice for self-employed individuals looking to maximize their retirement savings potential.
With an individual 401(k), self-employed individuals have the opportunity to contribute both as an employer and an employee, providing them with increased flexibility and the ability to save more for retirement.
“The individual 401(k) is an excellent retirement savings vehicle for self-employed individuals. It allows them to make higher contributions compared to other retirement plans and take advantage of valuable tax benefits. It’s a powerful tool for building a secure financial future.”John Smith, Financial Advisor
Contributing to an individual 401(k) allows self-employed individuals to benefit from tax advantages similar to those of traditional 401(k) plans. Contributions made as an employer are tax-deductible, reducing taxable income. Additionally, contributions made as an employee can be made on a pre-tax or after-tax basis, depending on the individual’s preference and tax situation.
A key advantage of individual 401(k)s is the higher contribution limits they offer. As of 2021, self-employed individuals can contribute up to $58,000 or 100% of their compensation, whichever is lower. For individuals age 50 and older, an additional catch-up contribution of $6,500 is allowed, bringing the total contribution limit to $64,500.
These higher contribution limits provide self-employed individuals with the opportunity to save more for retirement compared to traditional and Roth IRAs. By maximizing their contributions to an individual 401(k), self-employed individuals can accelerate their retirement savings and potentially achieve their financial goals sooner.
Benefits of Individual 401(k)s for Self-Employed Individuals:
- Higher contribution limits compared to traditional and Roth IRAs
- Flexibility to contribute as both an employer and an employee
- Opportunity for tax-deductible contributions
- Potential for accelerated retirement savings
Self-employed individuals are encouraged to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to determine if an individual 401(k) is the right retirement savings option for their specific needs and goals.

| Retirement Plan | Contribution Limits (2021) | Catch-Up Contributions (Age 50+) |
| Individual 401(k) | $58,000 or 100% of compensation, whichever is lower | $6,500 |
| Traditional IRA | $6,000 or $7,000 if age 50+ | N/A |
| Roth IRA | $6,000 or $7,000 if age 50+ | N/A |
Exploring SIMPLE IRAs
When it comes to retirement plans for small businesses, the SIMPLE IRA stands out as a cost-effective and hassle-free solution. Designed for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees, a SIMPLE IRA provides employers and employees with a simplified way to save for retirement.
One of the key benefits of a SIMPLE IRA is its tax-deductible contribution feature. This means that as an employer, you can deduct your contributions to the IRA on your business taxes, helping reduce your overall tax liability.
Employees are also eligible to make contributions to their SIMPLE IRAs on a pre-tax basis, allowing them to lower their taxable income for the year. It’s a win-win situation for both employers and employees, fostering a supportive retirement savings environment.
“A SIMPLE IRA can be a game-changer for small businesses. It offers a simplified way to offer retirement benefits to employees and an opportunity for tax savings.”-Financial Advisor
However, it’s important to note that while the contribution process is simplified, there are specific contribution limits for SIMPLE IRAs. As of 2022, the maximum contribution limit for employees is $14,000, with an additional $3,000 “catch-up” contribution allowed for those aged 50 and older.
Employers, on the other hand, have two options for their contributions. They can match their employees’ contributions dollar for dollar, up to 3% of the employee’s compensation, or they can make a non-elective contribution of 2% of each eligible employee’s compensation, regardless of whether the employee contributes to the plan or not.
Benefits of SIMPLE IRAs for Small Businesses:
- Simplified administration: SIMPLE IRAs are easy to set up and maintain, reducing administrative burdens for small business owners.
- Lower costs: Compared to other retirement plans, the administrative fees associated with SIMPLE IRAs are generally lower, making them a cost-effective retirement savings account.
- Flexibility: Employees have the freedom to choose how much they want to contribute to their SIMPLE IRAs, allowing for personalized retirement savings goals.
- Tax advantages: Both employer and employee contributions to a SIMPLE IRA are tax-deductible, providing potential tax savings.

As a small business owner, offering a SIMPLE IRA can be a powerful tool in attracting and retaining talented employees. The simplicity, flexibility, and tax advantages make it an appealing retirement savings option for both employers and employees.
In the next section, we will explore another type of IRA – inherited IRAs, and the rules and considerations surrounding these accounts.
Inherited IRAs
An inherited IRA is a retirement account that is passed down to a beneficiary after the original account holder’s death. The rules governing inherited IRAs can vary depending on the relationship to the deceased and the age of the beneficiary. It’s crucial for beneficiaries to have a clear understanding of the withdrawal rules and the tax implications associated with inheriting an IRA.
When it comes to an inherited IRA, the beneficiary becomes the new account holder and has several options for handling the account. These options may include taking a lump-sum distribution, setting up an inherited IRA, or disclaiming the inheritance altogether. The choice of what to do with the inherited IRA will depend on factors such as the beneficiary’s financial situation, future plans, and overall tax strategy.
Withdrawal Rules:
One of the key aspects of an inherited IRA is understanding the withdrawal rules. The IRS requires beneficiaries to withdraw a minimum amount from the inherited IRA each year, known as the required minimum distribution (RMD). The amount of the RMD is determined by the beneficiary’s age and life expectancy, and failure to take the RMD can result in significant tax penalties.
It’s important to note that the timing of the first RMD can vary depending on the relationship between the beneficiary and the deceased account holder. Spouses who inherit an IRA from their deceased spouse have the option to treat the IRA as their own and delay taking RMDs until they reach the age of 72. Non-spouse beneficiaries, on the other hand, typically need to start taking RMDs by December 31st of the year following the original account holder’s death.
The withdrawal rules for inherited IRAs can be complex, and it’s advisable for beneficiaries to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to ensure compliance and make informed decisions about their inherited retirement funds.
Tax Implications
Inherited IRAs have unique tax implications that beneficiaries should be aware of. While traditional IRAs are funded with pre-tax dollars and require taxes to be paid upon withdrawal, inherited IRAs have different tax treatment, emphasizing the importance of understanding the rules set by the Internal Revenue Service.
For non-spouse beneficiaries, withdrawals from an inherited IRA are generally subject to income tax. The tax rate is based on the beneficiary’s individual tax bracket, and it’s essential to plan for the potential tax liability. Additionally, inherited IRAs do not have the same penalty-free withdrawal exceptions as traditional and Roth IRAs, so beneficiaries should carefully consider their financial needs before making withdrawals.
It’s worth noting that Roth IRAs that are inherited have slightly different tax implications. Since Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars, qualified distributions from an inherited Roth IRA are generally tax-free. However, non-qualified distributions may be subject to income tax and penalties.
Ultimately, understanding the tax implications of an inherited IRA is critical for beneficiaries to effectively manage their retirement assets and maximize their savings.
“Inherited IRAs can provide a valuable source of retirement income for beneficiaries. However, it’s important to carefully navigate the withdrawal rules and tax implications to avoid unnecessary penalties and tax liabilities. Seek professional guidance to make informed decisions.”
To illustrate the potential tax implications of an inherited IRA, here is a table comparing the tax treatment for traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs:
| IRA Type | Tax Treatment for Beneficiaries |
| Traditional IRA | Taxed as ordinary income upon withdrawal |
| Roth IRA | Qualified distributions are tax-free; non-qualified distributions may be subject to income tax and penalties |

Understanding the rules and implications associated with inherited IRAs is crucial for beneficiaries who are tasked with managing these retirement accounts. By navigating withdrawal rules and considering tax implications, beneficiaries can make informed decisions about their inherited IRA and effectively plan for their own future retirement.
Exploring Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
While not technically an IRA, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) offer individuals a tax-advantaged solution to save for medical expenses. With rising healthcare costs, having a dedicated account for medical needs is crucial for financial planning. HSAs provide individuals with a triple tax advantage, making them a valuable tool for healthcare savings.
Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, which means that individuals can lower their taxable income by depositing funds into their account. This tax advantage allows for additional savings and potentially lower tax liabilities. It’s a win-win situation.
“Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, which means that individuals can lower their taxable income by depositing funds into their account.”
HSAs also offer tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. This means that individuals can use the funds in their HSA to pay for medical costs without incurring any additional tax burden. It’s an efficient and convenient way to handle medical expenses.
It’s important to note that HSAs can be used in conjunction with a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). These plans typically have lower monthly premiums but higher deductibles. The money saved on premiums can be put towards the HSA, creating a dedicated fund for medical expenses.
To illustrate the benefits of an HSA, here’s a breakdown of how it works:
| Benefits of an HSA | |
| 1. Tax-Deductible Contributions | Individuals can lower their taxable income by depositing funds into an HSA. |
| 2. Tax-Free Withdrawals | Funds in an HSA can be used tax-free for qualified medical expenses. |
| 3. Triple Tax Advantage | HSAs provide a tax break on contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. |
With an HSA, individuals have control over their healthcare funds. They can choose how much to contribute, how to invest the funds, and when to use them for medical expenses. It’s a flexible and tax-efficient way to save for healthcare costs in retirement.
It’s important to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to understand the specific rules and regulations surrounding HSAs and to determine if it’s the right option for your unique financial situation.

Diversifying with Alternative Investments
In addition to traditional investments, individuals can explore alternative investment options within their IRAs, such as mutual funds and brokerage services. This includes the ability to invest in alternative assets such as gold, bitcoin, and other cryptocurrencies. These alternative investment options introduce diversification and the potential for higher returns within a retirement account.
Diversification is a key strategy for IRAs. By diversifying your portfolio, you spread out your investments across different asset classes, reducing the impact of market volatility and potentially increasing the overall return on your investment. Alternative investments, such as gold IRAs, bitcoin IRAs, and cryptocurrency IRAs, provide unique opportunities for diversification.
Gold IRA: A gold IRA allows you to invest in physical gold, such as gold bars or coins, within your retirement account. Gold has long been considered a safe haven asset, with the potential to act as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty. Including gold in your IRA can provide stability and diversification to your overall retirement portfolio.
Bitcoin IRA and Cryptocurrency IRA: a novel account that integrates technological innovation into your retirement savings accounts. With the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, individuals now have the option to invest in digital currencies within their IRAs. While these investments come with higher volatility and risk, they also offer the potential for significant returns. Including Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies in your IRA can add a level of growth potential and technological innovation to your investment strategy, turning your IRA account into a tax-advantaged investment account focusing on future technologies.
It’s important to note that investing in alternative assets within an IRA may come with specific rules and regulations, so it’s crucial to consult with a financial advisor or IRA custodian to ensure compliance. Additionally, alternative investments may require specialized knowledge and expertise. Therefore, it’s advisable to seek guidance from professionals familiar with the specific asset class you are interested in.
Benefits of Alternative Investments in IRAs:
- Diversification of your retirement portfolio
- Potential for higher returns
- Opportunity to invest in unique assets
- Protection against inflation and economic uncertainty (in the case of gold)
- Exposure to new and innovative technologies (in the case of cryptocurrencies)
“By including alternative investments like gold, bitcoin, and other cryptocurrencies in your IRA, you can diversify your retirement portfolio and potentially increase your overall returns.”
As with any investment, it’s essential to understand the risks involved and conduct thorough research before allocating funds to alternative assets. While these investments can offer exciting opportunities, they may not be suitable for everyone, and individual circumstances should be taken into account.

Understanding Contribution Limits
When it comes to saving for retirement, it’s important to understand the contribution limits for different types of IRAs. The IRS sets specific limits for annual contributions, which may vary based on factors such as age, income, and employment status.
Traditional IRA Contribution Limits
For traditional IRAs, the maximum contribution limit for 2021 is $6,000 for individuals under the age of 50. However, individuals who are 50 years or older can make catch-up contributions of an additional $1,000, bringing the total limit to $7,000.
Roth IRA Contribution Limits
Roth IRAs also have a maximum contribution limit of $6,000 for individuals under 50 years old. Just like traditional IRAs, individuals who are 50 years or older can make catch-up contributions of an extra $1,000, allowing them to contribute up to $7,000.
Catch-Up Contributions
Catch-up contributions are available to individuals who are age 50 or older. This provision allows them to contribute additional funds to their IRAs above the regular annual limits. Catch-up contributions allow individuals to boost their retirement savings in the years leading up to retirement.
It’s important to note that these contribution limits are subject to change. To ensure you are aware of the current limits, consult the IRS website or speak with a financial advisor.
Maximizing Your Retirement Savings
Understanding and adhering to contribution limits is essential to maximize your retirement savings. By making regular contributions within the set limits, you can take advantage of the tax benefits and potential growth opportunities offered by both traditional and Roth IRAs. Consider reviewing your retirement plan regularly to ensure you are contributing the maximum amount allowed and making the most of your retirement savings journey.
Maximizing Tax Advantages
One of the key benefits of Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) is the array of tax advantages they offer. Whether it’s through tax-deductible contributions in traditional IRAs or tax-free withdrawals in Roth IRAs, understanding and utilizing these advantages can significantly boost your retirement savings.
Contributions made to traditional IRAs are often tax-deductible, which means you can potentially reduce your taxable income in the year you make the contribution. This deduction can lead to lower tax liabilities, effectively increasing the amount of money you can invest in your retirement. However, it’s important to note that the deductibility of contributions may be subject to income limits and employer-sponsored retirement plans.
On the other hand, Roth IRAs provide tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Since contributions to Roth IRAs are made with after-tax money, the earnings within the account can grow tax-free. This means that when you withdraw funds from your Roth IRA during retirement, you won’t owe any taxes on those funds. The tax-free nature of these withdrawals can be a significant advantage, providing you with a potentially larger pool of funds to support your retirement lifestyle.
By strategically choosing between traditional and Roth IRAs, individuals can optimize their tax advantages based on their current and future tax circumstances. Factors such as income level, tax rate, and retirement goals should be considered when determining which type of IRA to utilize.
Maximizing Deductions
In addition to the tax advantages offered by IRAs, there are other deductions that individuals can take advantage of to further enhance their retirement savings. For example, self-employed individuals who contribute to SEP IRAs can deduct their contributions as a business expense, reducing their overall taxable income. This deduction can provide a valuable opportunity for self-employed individuals to save for retirement while minimizing their tax burden.
It’s important to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to fully understand the tax advantages and deductions available to you based on your individual circumstances. They can help you navigate the complex tax rules and ensure that you’re making the most of the tax benefits offered by IRAs and other retirement savings vehicles.

Having a comprehensive understanding of the tax advantages and deductions associated with IRAs is crucial for maximizing your retirement savings. By utilizing the right IRA type and taking advantage of available deductions, you can optimize your tax situation while building a robust nest egg for your future.
Considering Small Business Retirement Plans
Small business owners have several retirement plan options available to them, such as SEP IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs, and individual 401(k)s. These employer-sponsored plans can help both the business owner and employees save for retirement while providing potential tax advantages.
One popular option is the SEP IRA, which stands for Simplified Employee Pension Individual Retirement Account. This plan is designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners. With a SEP IRA, contributions are tax-deductible and based on a percentage of income. The contribution limits for SEP IRAs are generally higher than those for traditional and Roth IRAs, allowing for greater retirement savings potential.
Another option is the SIMPLE IRA, which stands for Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees. This plan is specifically designed for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees. With a SIMPLE IRA, both the employer and the employee contribute to the retirement account. These contributions are tax-deductible and subject to specific contribution limits.
For self-employed individuals or business owners with no employees other than a spouse, the individual 401(k) is an attractive retirement plan option. Also known as a solo 401(k), this plan allows for higher contribution limits compared to traditional and Roth IRAs. It provides an opportunity for significant retirement savings while offering potential tax advantages.
Each of these small business retirement plans has its own set of rules, contribution limits, and tax advantages. It’s essential for small business owners to carefully evaluate their options and consider their specific needs and goals when choosing a retirement plan for themselves and their employees.
Benefits of Small Business Retirement Plans
The benefits of offering a small business retirement plan are numerous. For small business owners, participating in a retirement plan allows them to save for their own retirement while also attracting and retaining talented employees. It demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being and can help create a positive company culture.
Employees, on the other hand, benefit from the opportunity to save for their own retirement and take advantage of potential tax advantages. Having a retirement plan offered by their employer provides a sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that they are actively building their retirement savings.
By offering a small business retirement plan, both the employer and the employees can benefit from potential tax advantages. Contributions to these retirement plans are typically tax-deductible, which helps reduce the business owner’s taxable income. Additionally, the contributions made by employees may be made on a pre-tax basis, reducing their taxable income as well.
Comparing Small Business Retirement Plans
Here is a comparison of the key features of the different small business retirement plans:
| Plan Type | Eligibility | Contribution Limits | Employer Contributions | Employee Contributions | Tax Advantages |
| SEP IRA | Self-employed | Up to 25% of income or $58,000 in 2021 | Employer contributions only | N/A | Tax-deductible contributions |
| SIMPLE IRA | Small businesses with fewer than 100 employees | $13,500 in 2021 ($16,500 for individuals age 50 and older) | Employer contributions required | Employee contributions optional | Tax-deductible contributions |
| Individual 401(k) | Self-employed or business owners with no employees other than a spouse | $19,500 in 2021 ($26,000 for individuals age 50 and older) signifies the contribution limit for retirement savings accounts, including those that offer tax advantages. | Employer and employee contributions optional | Employee contributions optional | Tax-deductible contributions |

As you can see, each small business retirement plan has its own eligibility requirements and contribution limits. It’s crucial to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to determine which plan is the best fit for your specific business needs and retirement goals.
By offering a small business retirement plan and leveraging the potential tax advantages, small business owners can not only take care of their own retirement but also provide a valuable benefit to their employees. With careful planning and consideration, small businesses can pave the way for a secure and prosperous retirement for all.
Exploring IRS Regulations and Rules
When it comes to managing your retirement account, it’s crucial to understand the IRS regulations and rules that govern IRAs. These regulations cover various aspects, including contribution limits, withdrawal rules, and required minimum distributions (RMDs). Staying informed and complying with these regulations is essential to avoid penalties and make the most of your retirement savings.
Firstly, let’s talk about contribution limits. The IRS sets specific limits on how much you can contribute to your IRA each year. These limits differ based on factors such as your age, income, and the type of IRA you have. It’s important to be aware of these limits to ensure that you don’t exceed them and face potential tax consequences.
Secondly, withdrawal rules play a crucial role in managing your IRA. Depending on the type of IRA you have, there may be restrictions and penalties associated with early withdrawals. It is essential to understand these rules to avoid unnecessary fees and taxes. Remember, withdrawing funds from your retirement account too early may impact your long-term savings goals, including the benefits of compounding in tax-advantaged investment accounts.
Lastly, required minimum distributions (RMDs) are a critical aspect of IRA regulations. Once you reach a certain age, typically 72 years old, the IRS requires you to withdraw a minimum amount from your traditional IRA each year. Failing to take these distributions can result in significant tax penalties. Understanding the RMD rules and ensuring compliance is essential to avoid any unwanted financial consequences.
Overall, navigating IRS regulations and rules is vital to ensure that your retirement account remains compliant and optimized for your long-term goals. By staying informed and working with a financial professional, you can confidently navigate the intricacies of these regulations and make the most of your IRA.
IRS Regulations and Rules at a Glance:
| Aspect | Details |
| Contribution Limits | Varies based on age, income, and IRA type |
| Withdrawal Rules | Penalties for early withdrawals and restrictions on certain distributions |
| Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) | Mandatory withdrawals from traditional IRAs at a certain age |
Remember, consulting with a financial advisor or tax professional is always a wise decision when it comes to understanding and complying with IRS regulations. Their expertise can help you navigate the rules effectively and optimize your retirement savings strategy.

Making Informed Investment Decisions
When it comes to your IRA, making informed investment decisions is crucial for long-term success. By carefully considering your options and implementing effective strategies, you can maximize your retirement savings and achieve your financial goals.
Diversification for Risk Management
A key aspect of making informed investment decisions is diversifying your portfolio. Diversification involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. This strategy helps mitigate risk by reducing the impact of any single investment on your overall portfolio.
By diversifying, you can distribute your investments across a range of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. This approach helps cushion against market fluctuations and provides the potential for consistent returns over time.”Diversification is an essential risk management tool that allows you to manage potential losses while seeking opportunities for growth.”
Aligning Investments with Retirement Goals
When making investment decisions for your IRA, it’s crucial to align your choices with your specific retirement goals. Consider factors such as your desired retirement lifestyle, time horizon, and risk tolerance.
For example, if you have a longer time horizon until retirement, you may be more comfortable taking on some level of risk in pursuit of higher returns. On the other hand, if you are nearing retirement, you may want to focus on more conservative investments to protect your savings.
Seeking Professional Advice
While it’s possible to make investment decisions on your own, seeking advice from an experienced investment professional can provide valuable guidance. Financial advisors can help assess your risk tolerance, understand your retirement goals, and develop a tailored investment strategy for your IRA.
With their knowledge and expertise, investment professionals can help you navigate the complexities of the financial markets, identify suitable investment opportunities, and make confident decisions that align with your long-term goals.

Conclusion
To maximize retirement savings, it is essential to explore the various types of IRA investment options available. Understanding the benefits and features of each type allows individuals to make informed decisions in their retirement planning journey. By leveraging the different IRA investment types, individuals can build a well-diversified retirement portfolio that aligns with their goals.
Retirement planning requires careful consideration of IRA investment types. Traditional and Roth IRAs offer distinct tax advantages, while SEP IRAs are ideal for self-employed individuals. Self-directed IRAs provide flexibility in investment options, and individual 401(k)s offer higher contribution limits. For small business owners, SIMPLE IRAs can be a cost-effective choice.
It is crucial to stay up to date with IRS regulations and rules governing IRAs, including contribution limits and required minimum distributions. By adhering to these regulations, individuals can avoid penalties and fully utilize the benefits of their retirement accounts. Making informed investment decisions, with consideration for diversification and risk management, can further enhance retirement savings.
Ultimately, by exploring the different IRA investment types, individuals can maximize their retirement savings potential and work towards a financially secure future. Whether it is through traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, SEP IRAs, or other options, careful planning and strategic decision-making can help individuals achieve their retirement goals.
FAQ
What is a traditional IRA?
A traditional IRA is a retirement account that allows individuals to make tax-deductible contributions and enjoy tax-deferred growth until withdrawals in retirement.
How does a Roth IRA differ from a traditional IRA?
Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax money, but qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, providing a valuable tool for tax-free retirement savings.
Who can benefit from a SEP IRA?
SEP IRAs are designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners who want to make higher contributions to their retirement savings.
What are the advantages of a self-directed IRA?
A self-directed IRA allows individuals to invest in a wide range of assets beyond traditional stocks and bonds, providing greater control over investment decisions and unique opportunities for growth.
What is an individual 401(k) or solo 401(k)?
An individual 401(k) is a retirement plan designed for self-employed individuals or business owners with no employees other than a spouse, offering higher contribution limits compared to traditional and Roth IRAs.
What are SIMPLE IRAs, and who are they suitable for?
SIMPLE IRAs are retirement plans designed for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees, providing a simplified and cost-effective way to offer retirement benefits. They are suitable for businesses looking to save for retirement while providing potential tax advantages.
How do inherited IRAs work?
Inherited IRAs are retirement accounts inherited from a deceased individual, and the rules surrounding them vary depending on the relationship to the original account holder and the age of the beneficiary.
What are the benefits of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)?
HSAs provide individuals with a tax-advantaged way to save for medical expenses, with contributions being tax-deductible and qualified withdrawals for medical expenses being tax-free.
Can I invest in alternative assets such as gold or cryptocurrencies with my IRA?
Yes, with a self-directed IRA, you can invest in alternative assets like gold, bitcoin, and other cryptocurrencies, allowing for greater diversification and potential for higher returns within a retirement account.
What are the contribution limits for IRAs?
The IRS sets specific contribution limits for different types of IRAs, which may vary depending on factors such as age, income, and employment status.
What are the tax advantages of IRAs?
IRAs provide tax advantages such as tax-deductible contributions (in the case of traditional IRAs) and tax-free withdrawals (in the case of Roth IRAs), allowing individuals to save on taxes while building their retirement savings.
What retirement plan options are available for small business owners?
Small business owners have several retirement plan options available, including SEP IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs, and individual 401(k)s, which can help both the business owner and employees save for retirement while providing potential tax advantages.
What regulations and rules do I need to consider for my IRA?
The IRS has specific regulations and rules governing IRAs, such as contribution limits, withdrawal rules, and required minimum distributions. It’s important to stay informed and comply with these regulations to avoid penalties and maximize the benefits of your retirement account.
How can I make informed investment decisions for my IRA?
When selecting investments for your IRA, it’s important to consider diversifying your portfolio to manage risk and align your investments with your retirement goals. Seeking advice from an investment professional can also help you make confident and strategic investment decisions.